
Understanding Electricity Bill
BEFORE OPTING FOR ROOFTOP SOLAR POWER
Understanding electricity bill is as important as paying them on time.
Most of the consumers fail to understand their electricity bills, and pay them by only looking at the total amount and due date.

There are various components and factors that combine to your bills.
These factors have a lot of information and insights to provide into your energy consumption pattern and behavior.
Energy consumption patterns are different for each user.
And these patterns vary seasonally, as the demand for power surges during summer months for running Air conditioners, the same declines drastically in winter months as the only heavy appliances working in cold weather are heaters.
NOW,
Let us Understand what all factors play a major role in comprising your electricity bill.
Tariff Category –
This is the category on which you are provided an electrical connection from the electricity distribution company.
this category decides most of the other factors and components in your billing format.
this category is split into 2 major domains
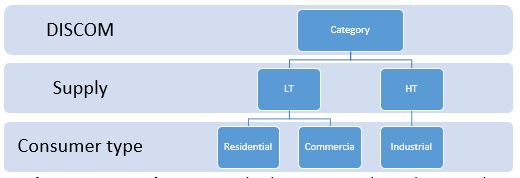
LT – low tension supply – 230v single phase or 400 v three phase supply.
this is usually provided to residential consumers, commercial consumers- such as retail shops. Offices etc, and small scale industrial consumers – small manufacturing or processing units.
HT supply – High tension supply – 11kv and above. Here a transformer is provided just outside your premises for step down of the supply voltage from distribution company.
usually apartment complexes, schools, large offices, townships all have 11kv supply.
further – this category has another split – that decides the nature of you as a consumer,
residential consumer– labeled as domestic
Commercial consumer – labeled as non-domestic/commercial
Industrial consumer – labeled as Industrial.
a Fixed tariff , that has to paid regardless of how many units of electricity you consume or not is decided from this component of the bill.
a Fixed tariff is higher for industrial consumer, and attracts another tariff as transformer rent charges.

Connected load or Sanctioned load
this is self-explanatory – this tells us about the total connected load of your premises, the same is asked for to the distribution company,
say my total load if whole building appliances are switched on simultaneously at a single time
is 100 kW, this is my total consumption capacity – I will ask the grid supply or the distribution company to sanction my load supply for 100 + 25% (future expansion + developments)
so my sanctioned load would be 125kw
We will have to pay a security deposit to the electricity company when asking for connectivity to their grid lines and distribution stations.
this permission for sanctioned load varies on Constructed area, assessment of power needs for now and future, based on how much units of electricity will be consumed monthly
based on this the electricity company sets up their poles and wires in your area to provide you with a connection.
Units Consumed
units consumed is measured in KWH ( kilo – watt- hour)
this can be broken down into another concept on it’s own.
1 units = 1 KWH
to understand 1KWH – it is a value that is derived from the power rating on your appliances.
if an appliance consumes 1000 watts(1 tn AC ) and is switched on for 1 hour
then we will say the appliance consumes 1KW power.
in one hour it consumes 1 unit of electricity
similarly – in 100 hours of it’s operation , it consumes 100 units of electricity.
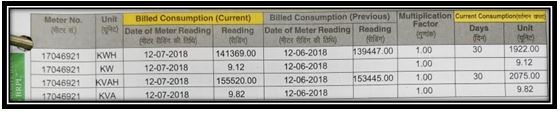
The units provided in your monthly bills are based on the difference in readings to your previous month meter reading and your current month meter reading.
In Industrial connections, these units are often derived from another sibling of Unit (KWH)
named KVAH
this sibling of KWH is calculated with another Factor that plays a crucial role in energy efficiency.
Called POWER FACTOR – power factor is best explained with this image
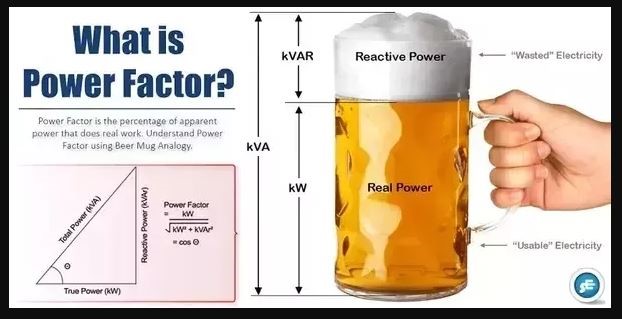
when you are running an inductive load or a capacitive load,
this power factor can be leading or lagging, meaning, some power is wasted in converting your electricity into mechanical energy or kinetic energy ( inductive load)
or it is wasted in form of head or leaking charge current ( capacitive load)
So let’s see KVAH ( kilovolt amp-hour )
self-explanatory – voltage supply X Current (Amp(consumed by the appliance)) X hour
say the AC of 1000 Watts – when it is switched on Draws 1300 watts from the supply, then when it is operational, it works hard to bring down the temperature of your room as per requirement
say 24 degrees C , then when the temperature of 24 degrees is achieved, the AC doesn’t have to work at full 100%, it will draw only 700 watts,
the time it took for AC to Start, decides the power factor to be leading or lagging,
PF should be about 0.85 ~ 0.9
for industries with heavy electrical motors and loads – PF should not be below 0.75
else you attract penalties from the Electricity Regulators and Distribution companies.
this is because if your PF is not near ideal, you are causing a lot of losses in transmission lines, causing degradation of the transformers in your locality, causing grid voltage fluctuations.
KVAH = KWH/PF
UNDERSTANDING ELECTRICITY BILL
TARIFF STRUCTURE –
TARIFF STRUCTURE
One of the most important highlights on your bill.
the main thing that decided your bills.
this block tells you where your main expenses occur, how much units you consume etc.. and how your bill can be reduced
Typically for residential connections – the structure is slab based
and for industrial connections – it is high price flat rate with no slabs.
What are these slabs you ask ?
these are the sub categories created by DISCOMS ( distribution companies)
This is done to provide lower bills to consumers who consume less units in a billing cycle.
and charge extra/ variable prices to consumers who consume more power , based on their consumption.
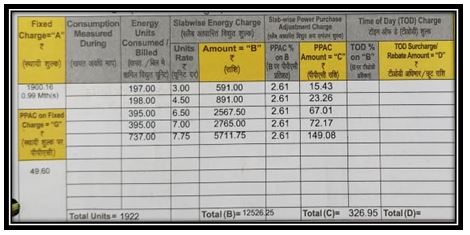
say your unit price is decided on the quota of units you have consumed.
for first 200 units say 3.rs/ unit
for next 400 units say 4.5 rs / unit
for next 400 units say 6.5 rs / unit
and so on………
Fuel Adjustment charges
FAC ( the surcharge charges )
these are levied on all slabs and fixed tariffs as well.
this is the extra cost of power incurred by DISCOMs due to increase in fuel prices every month, or year, as we all know fossil fuels are limited, coal and oil are imported from various parts of india and the world to thermal power plants to create electricity, so the surcharge is a added security net for the discom against volatile market prices for raw material.
these FAC charges are increasing at 3% year on year.
as per estimates by 2030 these charges will be 50% higher than what they are today in 2020.
as we all know Coal and oil prices are dependent on consumption and supply, and we will bear the expensive electricity unless our government or discoms find a cheaper alternative source of electricity that is not dependent on the the import of raw materials and doesn’t need regular raw material input .
namely Renewable energy technologies hold the key to unlock this saving potential.
Solar energy, wind energy, geo thermal energy, these all forms of energy are cheaper than fossil fuel derived energy.
when we have a 100% grid powered from renewable energy sources, FAC will be obsolete.
Electricity Duty/ taxes
each state in india levies electricity duty on each tariff, unit, fixed and slabs.
then there are electricity taxes aswell.
this duty is not subject to GST yet in 2020, each state has different tax rate, based on the revenue they need to generate from electricity grid.
Mostly this DUTY/ TAX is as follows
this tax is 5% flat on fixed tariff
8 % on the unit slabs
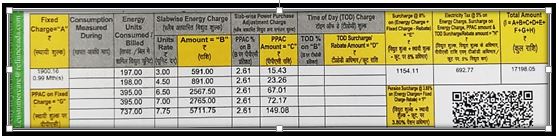
and another Pension tax is claimed by some state governments for their employees retirement funds
the pension tax is 3.8% to 5% depending on the state.
All in all a consumer ends up paying 13 to 18% tax on their electricity consumptions.
which is very high as compared to other commodities , this a consumer purchases everyday.
| Industrial including mining | 8 p/unit |
| Agriculture (i) In the case of metered supply (ii) In the case of non-metered supply | 1 p/unit 5% of the flat rate |
| Commercial, domestic and others | 6 p/unit |
| Consumption under temporary connection | 15 p/unit |
| Consumption of self-generated energy of any purpose | 6 p/unit |
These were the basic categories to understand your electricity bill.
by understanding it , you are in a better position to assess if you are being charged wrongly.
if you are paying high bills and should not have been paying high bills.
if you could save your money by following few patterns and reduce your electricity bills.
if you should consider generating your own power and take your electricity needs into your own hands
if you are taking the decision to opt for solar power , how should you go about it ?
we answer these in detail in this video
click on the link below.




Leave a Reply